Maybe among friends all there may still be confused as to what the diffrence handphone Symbian with java? Or maybe there are not know or confused actually Handphone temen2 it includes symbian or java ?Well, from the temen2 confused, here I will explain a little difference between the two Handphone.
Symbian OS is an open operating system developed by Symbian Ltd. Designed for use by mobile devices (mobile). Advantages of Hp Symbian, among others:
1. Hp Symbian can already rich multitasking computer, meaning Hp Symbian can open more than one application in standby. So, if there are incoming sms, temen2 ga must be out of the applications that are currently in use to read the sms.
2. Has its own menu button.
3. Hp Symbian usually have the ability to read RAM better than Hp Java. So if you surf, open a large file so much faster.
4. Have two kinds of installers, namely Java (.jad / .jar) and symbian itself (.sis).
5. Can copy and paste (copy and paste) rich computer.
6. Order the menu can be set alone.
7. Game over real appear (depending on the type / types Hp her).
8. Handphone Symbian be reproduced capabilities with the addition of third-party applications, because systemnya open. For example Hp Symbian temen2 can not to play the video with .avi format, temen2 stay put / install applications that can be to play the .avi format. (Hp Symbian classified or so-called smartphones).
The weakness of Hp Symbian is:
1. Because it has an open operating system, Hp type is very vulnerable to viruses such as Cabir, Commwarior, SymbOS.skulls. and much more.
2. Hp with this system is also easy to Hang or later alias slow in opening the gallery, songs, and short messages (SMS).
Meanwhile, Hp with a closed operating system is the operating system Hp JAVA or also called Hp Java. This phone only supports apps and games in .jar format. The disadvantage is that HP is not able to freely inserted or installed all kinds of applications. The advantages are:
1. This phone can not have a virus handphone.
2. Not easy to hang like Hp with Symbian OS.
Sunday, November 30, 2014
Wednesday, November 12, 2014
Hardware Components of a Computer
Computer hardware (computer hardware) is the physical components that make up an integrated system of Personal Computer (PC).
Typically these devices are assembled and largely incorporated into a computer case and others are outside the casing.
The hardware inside the casing generally consists of:
Motherboard (main board)
MotherboardMotherboard / mainboard is a key component to build a computer. Square-shaped board with slots to include other components. Its function is to connect all components of the PC. Other computer hardware are all attached directly to the motherboard slot or at least connected using a cable.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Random Access Memory (RAM) RAM serves as a transit point to provisional data for the operations being carried out by the CPU. RAM is volatile, meaning that this device does not store data permanently, just for the required operation only. RAM capacity on the PC that we often find quite diverse, ranging from 256 MB (megabytes) - 16 GB (GigaBytes)
Video Graphics Array (VGA)
CardVGA VGA card or graphics card serves as a link that allows the transmission of data between a PC and a graphical display device such as a monitor or projector. Most computers have a separate VGA as expansion cards installed on the motherboard slot. But there is also a computer that has an integrated VGA on the motherboard or on its CPU.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
Hard-disk DiskHard serves as a primary data storage in a computer system. Operating systems, applications, and documents stored on the hard-disks. In the latest PC, there are also new hardware called Solid State Drive (SSD). Functions the same as the hard-disk, but offers data transfer speeds faster.
Optical DriveOptical regular drive is also known as a CD drive, DVD drive, or ODD. The function of this device is to read and also save data to and from optical disc media such as CDs, DVDs, or Blu-Ray Disc.
Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Power Supply UnitPower Supply serves as a converter and distributor of electrical energy from the power outlet (eg PLN) to the form of electrical energy that can be used to run the computer components inside the casing. Typically, this PSU is placed at the back of the casing.
Aside from computer hardware contained within the casing, there are also common components we see outside the casing:
MonitorDisebut also screen or display. The function of the screen is to display video and graphical information generated from a computer via a tool called a graphics card (VGA Card). This monitor physical form similar to the television, television usually only capable of displaying graphical information with higher resolution size.
Keyboard and Mouse
Keyboard and mouse MouseKeyboard and serves as an input device to enter text commands, character, or move objects on a graphical interface to be processed by a computer. The size and shape of the tool is quite diverse, but its function is the same.
Beyond the components that we have already mentioned above, there are also computer hardware that not all computers have it:
UPSSering referred to as a battery backup, UPS primary function is to store and provide power backup that will be used when the main power source goes out. Aside from being a power reserve, most UPS also serves as a "stabilizer" that regulates the flow of electricity to fit the needs.
Printer and Scanner
PrinterPrinter serves as a print output of electronic documents both text and graphics. At home computers typically use paper as the print media. While the scanner function is the inverse of the printer that scans the data input from the outside of the computer into electronic form that can be processed digitally.
Speaker
The function of the speaker as the output device is a computer-generated voice. In addition to the speakers, often we find people who use headphones / headset as the sound output device.
Sound Card (voice)
Function as a liaison between the computer and the audio output device such as speakers
Modem
This tool is used to connect a computer to the internet
LAN Card
Function as a liaison computers in a network.
Motherboard components and Functions
Motherboard, or often also we know the name mainboard, motherboard, MB, or system board is a hardware device in the computer system in the form of printed circuit board (PCB).
Its function is to connect all components of a computer. The motherboard can be regarded as the backbone (backbone) of the computer system, all components of a computer is definitely connected to the motherboard, either directly or indirectly.
Motherboards are produced in a variety of sizes, some made specific to a particular system brand. However, most modern mobo made to ready fitted to a wide range of casing sizes. Mobo is installed inside the casing with the facing side of the casing is easy to open, and tightened with a screw.
The parts of the motherboard:
chipset
The first and most important part of a motherboard chipset, which serves as a liaison between the processor interface with various external components and buses. This chipset can determine and assess the features and capabilities of a motherboard.
There are two groups of common chipsets we have encountered in the market. Intel chipset group, which can only be used for Intel CPUs, and AMD chipsets for AMD processor output. Both groups were subdivided to various types of generation chipset that continues to grow.
Socket / CPU Slots
Socket is a "bersemayamnya" processor on the motherboard. Just like chipset, socket is also divided on the various types, depending on the type of processor supports.
Basic Input Output System (BIOS) chip
BIOS is a chip that stores the software to control the hardware and serves as an interface between the hardware and the operating system (OS). BIOS used by the computer to prepare prosess boot (startup) and check the readiness of the system and hardware before the computer starts.
Complimentary Metal Oxide Semicondutor (CMOS) Battery
CMOS is a battery to supply power to a small memory on the motherboard that is used to store computer configuration settings, time, etc. CMOS maintain that we do not need to configure these things every time we turn on the computer
memory Slots
Shaped slots rather long and slender serves as a place-install it Random Access Memory (RAM). In the modern computer era, almost all motherboard has at least two RAM slots, even on high-end computer specs there motherboards are equipped to 6 RAM slots.
VGA Slots (Graphic Card Slot)
This slot is used to install the components of a graphics card (video card). In modern computers, generally in the form of slots with PCI-Express interface. In the high-end motherboard can accommodate up to 3 slot graphics card.
expansion Slots
Expansion slots used to install additional devices such as sound card, LAN card, etc.
Storage Drive Connector
Its function is to connect storage devices like Hard Drive, Optical Drive, SSD, and external storage devices. Usually in the form of interface S-ATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) / ATA.
Other Ports
In addition to slots above, there are several ports on the motherboard which is very essential functions such as:
Back panel has several connectors are commonly encountered are :
Its function is to connect all components of a computer. The motherboard can be regarded as the backbone (backbone) of the computer system, all components of a computer is definitely connected to the motherboard, either directly or indirectly.
Motherboards are produced in a variety of sizes, some made specific to a particular system brand. However, most modern mobo made to ready fitted to a wide range of casing sizes. Mobo is installed inside the casing with the facing side of the casing is easy to open, and tightened with a screw.
| motherboard |
The parts of the motherboard:
chipset
The first and most important part of a motherboard chipset, which serves as a liaison between the processor interface with various external components and buses. This chipset can determine and assess the features and capabilities of a motherboard.
There are two groups of common chipsets we have encountered in the market. Intel chipset group, which can only be used for Intel CPUs, and AMD chipsets for AMD processor output. Both groups were subdivided to various types of generation chipset that continues to grow.
Socket / CPU Slots
Socket is a "bersemayamnya" processor on the motherboard. Just like chipset, socket is also divided on the various types, depending on the type of processor supports.
Basic Input Output System (BIOS) chip
BIOS is a chip that stores the software to control the hardware and serves as an interface between the hardware and the operating system (OS). BIOS used by the computer to prepare prosess boot (startup) and check the readiness of the system and hardware before the computer starts.
Complimentary Metal Oxide Semicondutor (CMOS) Battery
CMOS is a battery to supply power to a small memory on the motherboard that is used to store computer configuration settings, time, etc. CMOS maintain that we do not need to configure these things every time we turn on the computer
memory Slots
Shaped slots rather long and slender serves as a place-install it Random Access Memory (RAM). In the modern computer era, almost all motherboard has at least two RAM slots, even on high-end computer specs there motherboards are equipped to 6 RAM slots.
VGA Slots (Graphic Card Slot)
This slot is used to install the components of a graphics card (video card). In modern computers, generally in the form of slots with PCI-Express interface. In the high-end motherboard can accommodate up to 3 slot graphics card.
expansion Slots
Expansion slots used to install additional devices such as sound card, LAN card, etc.
Storage Drive Connector
Its function is to connect storage devices like Hard Drive, Optical Drive, SSD, and external storage devices. Usually in the form of interface S-ATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) / ATA.
Other Ports
In addition to slots above, there are several ports on the motherboard which is very essential functions such as:
- Pin power port 24/20 Pin - to connect the motherboard to the power supply unit (PSU).
- Port Power 4pin / 6pin - to supply power to the processor.
- Port for the power / reset on the front of the casing.
- Front connector port for USB and Front Audio.
Back Panel I / O
Back Panel I / O on the motherboard of the brand MSI
|
Back panel has several connectors are commonly encountered are :
- PS / 2 port - port for connecting a mouse / keyboard.
- USB Port - The port to connect peripherals with USB interface.
- S / PDIF port - Connect the audio connector S / PDIF
- RJ-45 Lan Port - Connect the LAN network cable
- Audio Port - Connects to the motherboard audio system / speakers.
- etc.
Tuesday, November 11, 2014
What is the motherboard?

Understanding the Inside Motherboard
The motherboard or mainboard is also commonly called a main board where there are components and chip controller responsible for managing data traffic in the system motherboard. Common functions of the motherboard is a pair processor, RAM, VGA Card, Sound Card, Internal Modem, and others.
Based on the use of the processor, motherboard (mobo) is divided into three parts, namely:
- For Dual Processor
- For Intel Processor
- For AMD Processor
A motherboard there are several components such as:
- Processor socket
- chipset
- Bus Controller
- Memory slot
- Expansion slot
- Port Drive
- BIOS
- ROM
- Power Connector
| motherboard |
Form Factor Motherboard
The motherboard has a characteristic and different sizes, which we commonly refer to the form factor.
| Form Factor Comparison |
The figure shows that the mobo has a different size.
Here is a comparison table of various kinds of form factors from Mobo:
Name PCB size (mm)
WTX 356 × 425
AT 350 × 305
Baby- AT 330 × 216
BTX 325 × 266
ATX 305 × 244
EATX (Extended) 305 × 330
LPX 330 × 229
microBTX 264 × 267
NLX 254 × 228
Ultra ATX 244 ×?
microATX 244 × 244
DTX 44 × 203
FlexATX 229 × 191
Mini-DTX 203 × 170
EBX 203 × 146
microATX 171 × 171
Mini-ITX 170 × 170
EPIC (Express) 165 × 115
ESM 149 × 71
Nano-ITX 120 × 120
COM Express 125 × 95
ESMexpress 125 × 95
ETX / XTX 114 × 95
Pico-ITX 100 × 72
PC / 10 (-plus) 96 × 90
ESMini 95 × 55
Beagle Board 76 × 76
Mobile-ITX 60 × 60
CoreExpress 58 × 65
Motherboards Pictured above is the form factors to the difference of the various dimensions of the size of the motherboard.
| Formfactors |
Specifications Motherboard:
In the selection of the motherboard, of course, we must consider several things. This will determine the specifications of the computers we use, namely:
- Processor support is used, use a slot or socket.
- Internal Speed Cache Memory, like 512 Kb, 1 Mb, 2 Mb, etc. The larger capacity also tightened the process.
- Upgrading can be done, be it to the processor, amount of RAM, etc.
- The number of slots available, Memory Slot, Expansion Slots: ISA, PCI, AGP or PCI Express.
- What supports VGA Card, Audio Card, LAN Card Onboard?
- Support The motherboard settings via jumper or BIOS.
what is a modem?
Many types - the type of modem that existed at this time, the modem can be distinguished based on the type of installation and network. if based on modem installation can be divided into an internal modem and an external modem while the modem based network can be divided into the cable modem with the media and meodem with wireless media.
- Internal modem is a card attached to the motherboard slot. advantage of this modem is way easy installation and the price is relatively cheaper.
- External modem is a modem that is installed outside the computer, usually plugged into the USB slot.
- Cable modem that uses media that sebuahmodem wired as a media intermediary (eg, cable TV and telephone network)
- Without a cable modem, this modem uses wireless media to the intermediary (eg, a GSM modem, Modem CDMA and others)
The history of mobile phones and its development

Cell phone or mobile phone today has mushroomed as with a laptop or computer. Neither of elementary school children to grandparents now use mobile phones to communicate. But if anyone knows who the inventor of the cell phone or the mobile phone itself ?? Sharing this time I will discuss about the history of mobile phones or mobile phones.
Definition
Cell phone or mobile phone or cell phone is an electronic telecommunications device that has the same basic capabilities with conventional fixed-line telephone, but can be taken anywhere (portable, mobile) and does not need to be connected to the network using a wired telephone (Wireless; LAN). Indonesia currently has two mobile phone network is the GSM system (Global System for Mobile Telecommunications) and system of CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access). Governing bodies of Indonesian cellular telecommunications is Indonesian Cellular Telecommunications Association (ATSI).
History
According to wiki aunt Indonesia inventor of the first mobile phone system is Martin Cooper, a Motorola factory workers on April 3, 1973, though often touted inventor of the mobile phone is a team from one division of Motorola (a division of Cooper's work) with the first model is DynaTAC. The idea proposed by Cooper is a communication tool that is small and easy to carry travel flexibly.
Cooper and his team face the challenge of how to include all electronic material into small-sized tool for the first time. Finally a first mobile phone was successfully completed with a total weight of weighing two kilograms. To make, manufacturer Motorola will cost approximately US $ 1 million. "In 1983, the portable cellular phone valued at US $ 4 thousand (Rp36 million), equivalent to US $ 10 thousand (Rp90 million).
After successfully producing the cell phone, the next biggest challenge is to adapt the infrastructure to support the communication system of the cell phone by creating a network system that only requires 3 MHz spectrum, the equivalent of five TV channels are channeled to the rest of the world.
Other figures are known to be very instrumental in the world of mobile communications is Amos Joel Jr. who was born in Philadelphia, March 12, 1918, he was recognized worldwide as an expert in the field of switching. He received a bachelor's degree (1940) and master's (1942) in electrical engineering from MIT. Shortly after the study, he began his career over 43 years (from July 1940-March 1983) at the Bell Telephone Laboratories, where he received more than 70 US patents in the field of telecommunications, particularly in switching. Amos E Joel Jr., making the system connector (switching) cell phone from one region to another region of the cell. Switching this should work when mobile users move or move from one cell to another so that the conversation is not interrupted. Since the discovery of this Joel Amos cell phone use be comfortable.
Development
The early generation
The history of the discovery of a cell phone can not be separated from the development of radio. Early discovery of cellular phones began in 1921 when the Detroit Michigan Police Department tried to use the phone one-way car. Then, in 1928 the Detroit Police Department began using a one-way radio communication on all patrol cars with a frequency of 2MHz.
In further developments, radio evolved into a two-way communication with the '' frequency modulated '' (FM).
In 1940, Galvin Manufactory Corporation (now Motorola) to develop portable handie-talkie SCR536, which means a communication tool on the battlefield during World War II. This period is the next generation of mobile phone 0 or 0-G, where cell phones were introduced.
After removing the SCR536, then in 1943 returned Galvin Manufactory Corporation issued a two-way radio FM partable first named SCR300 backpack model for the US Army's equipment weighs about 35 pounds and be able to work effectively within the operating range of 10 to 20 miles.
Mobile phone system 0-G still uses a VHF radio system to connect the phone directly to PSTNlandline. The weakness of this system is the problem of network congestion which then led to efforts to change the system.
Generation 0 ended with the invention of the modern concept by engineers from Bell Labs in 1947. They found the concept of using hexagonal phone as a basic cell phone. However, this new concept was developed in the 1960s.
Generation 1
The first generation of mobile phones also called 1G. 1-G is the first actual cell phone. In 1973, Martin Cooper of Motorola Corp. found a cell phone first and introduced to the public on April 3, 1973. The cell phone that was found by Cooper weighs 30 ounces or about 800 grams. This discovery has changed the world forever. The technology used is 1-G is still analog and known as AMPS. AMPS uses frequency between 894 MHz and 825 Mhz- operated at Band800 Mhz. Because it is analog, the system used is regional. One drawback generation 1-G is because the size is too big to be held by hand. The large size is due to the need of energy and poor battery performance. In addition, generation 1-G still has problems with mobility users. When placing a call, the user mobility is limited to coverage area of a mobile phone.
Generation 2
The second generation or 2-G appeared in about the 1990s. 2G in the US are already using CDMA technology, while in Europe, uses GSM technology. Uses standard GSM frequencies of 900 MHz and 1800 MHz frequencies. With these frequencies, GSM has a capacity greater customer. On the 2G generation analog signal has been replaced with a digital signal. The use of digital signal equip cell phones with voice mail, call waiting, and SMS.
Mobile phones in this generation also has a smaller size and lighter due to the use of digital chip technology. The smaller size is also due to the power requirements of smaller batteries. Advantages of generation 2G is the size and weight of the smaller and lower radio signals, thus reducing the harmful effects of radiation users.
Beneration 3
This generation is also called 3G that allows network operators to give their users a wider range, including internet video calls as well as high-tech. Within there are 3 standard for 3G telecom world ie Enhance datarates for GSM Evolution (EDGE), Wideband-CDMA and CDMA 2000 3G generation downside of this is the relatively higher costs, and the lack of network coverage because it is still new technology. But the interesting thing in this generation is to start the inclusion of the operating system on a mobile phone so as to make the phone features a full PC functionality even close. The operating system used, among others, Symbian, Android and Windows Mobile
Generation 4
This generation is also called Fourth Generation (4G). 4G is a phone system that offers a new approach and infrastructure solutions that integrate wireless technologies that already exist, including wireless broadband (WiBro), 802.16e, CDMA, wireless LAN, Bluetooth, and others. 4G systems based on the heterogeneity of IP networks that allow users to use multiple systems anytime and anywhere. 4G also gives its users high speed, high volume, good quality, global reach, and flexibility to explore a variety of different technologies. Finally, 4G provide fast data delivery services to accommodate various multimedia applications such as video conferencing, online gaming, and others.
5 generations of computers
Computers are tools used to process the data according to procedures that have been formulated. Computer word originally used to describe people whose jobs do arithmetic calculations, with or without the tools, but the meaning of the word is then transferred to the machine itself. Origins, processing information almost exclusively related to arithmetical problems, but modern computers are used for many tasks unrelated to mathematics.
Broadly, the computer can be defined as an electronic device that consists of several components, which can work together between the components with one another to produce a program based on the information and data. The computer components are included: Screen Monitor, CPU, Keyboard, Mouse and Printer. Without a computer printer can still do its job as a data processor, but the extent has not been seen on screen in print form.
In such a definition there are tools such as slide rules, mechanical calculators types ranging from abacus and so on, until all contemporary electronic computers. The term better suited for a broad sense such as "computer" is "that process information" or "information processing systems."
Nowadays, computers are becoming more sophisticated. But, before the computer is not small, sophisticated, cool and light now. In the history of computers, there are five generations in the history of computers.
1. First Generation (1944-1959)
Vacuum tubes as a signal amplifier, is a hallmark of the first generation. At first, the vacuum tube (vacuum-tube) is used as a component of a signal amplifier. The raw material consists of glass, so many have drawbacks, such as: easy to break, and easy to distribute the heat. This heat needs to be neutralized by the other component that serves as a coolant.
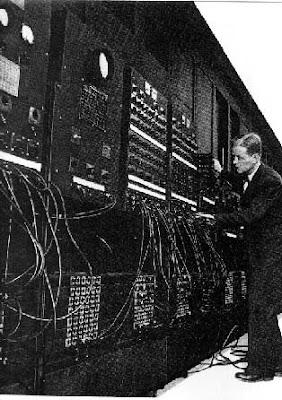
And the presence of additional components, existing computer eventually becomes large, heavy and expensive. In 1946, the electronic computer in the world that the ENIAC was finished first. On the computer contained 18,800 vacuum tubes and weighs 30 tons. so great in size, to the point that requires a separate classroom.
In the images appear ENIAC computer, which is the world's first electronic computer which has a weight weighing 30 tons, a length of 30 M and 2.4 M high and requires 174 kilowatts of electrical power.
2. Second Generation (1960-1964)

Transistors are characteristic of second generation computers. The raw material consists of three layers, namely: "basic", "collector" and "emmiter". Transistor is an acronym for Transfer Resistor, which means to influence the survival of two of the three layers, the power (resistor) which is in the next layer can also be affected. Thus, the function of the transistor is as a signal amplifier. As a solid component, tansistor has many advantages such as: not easily broken, do not conduct heat. And thus, existing computers become smaller and cheaper.
In 1960, IBM introduced the first commercial computer that utilizes a transistor and is used widely began circulating in the market. IBM-7090 computer made in the United States is one of the commercial computer utilizing transistors. The computer is designed to solve all sorts of jobs both scientific and commercial. Because of its speed and ability, led to the IBM 7090 became very popular. Other second-generation computers are: IBM Serie 1400, Serie NCR 304, MARK IV and Honeywell Model 800.
3. Third Generation (1964-1975)

The concept of the smaller and more affordable than transistors, eventually spurring people to continue doing various studies. Thousands of transistors finally managed combined in a very small form. Yag silicium piece has the size of several millimeters successfully created, and this is referred to as integrated circuit or IC-Chip which is the hallmark of the third generation computers. The magnetic ring may be the magnetization in one direction or the opposite, and finally download sinyalkan condition "ON" or "OFF" which is then translated into the concept of 0 and 1 in the binary number system which is needed by the computer. In every field there are 924 ring of magnetic memory, each of which represents one bit of information. Millions of bits of information currently residing in one single chip with very small form.
The computer used for automation was first introduced in 1968 by PDC 808, which has a 4 KB (kilo-byte) memory and 8 bits for memory cores.
4. The Fourth Generation (1975-Present)

Microprocessor is a typical Chiri fourth generation computer which is compacting thousands IC into a Chip. Because the forms are getting smaller and increasing the capability and the price offered is also getting cheaper. Microprocessor is the beginning of the birth of the personal computer.
In 1971, Intel Corp later developed the first microprocessor serie 4004. An example of this is the generation of the Apple I Computer, developed by Steve Wozniak and Steve Jobs by inserting the microprocessor on the circuit board of the computer. In addition, later appearing with the TRS 80 Model type Motorola 68000 processor and Zilog Z-80 uses 64KB of RAM standard. Apple II computers that use e-6502R processor type and by 64 Kb Ram, also a very popular PC at that time. Operating systems used are: CP / M 8 Bit. This computer is very popular in the early 80s.
IBM Personal Computer began issuing in about the year 1981, using the MS-DOS Operating System 16 Bit. Due to the price offered is not much different from the other computer, in addition to the technology is much better and bigger than IBM's own name, then in a very short time, the computer is becoming very popular.
5. Fifth Generation (Now - Future)

In this generation is characterized by the emergence of: LSI (Large Scale Integration) which is the solidification of thousands microprocessor into a microprocesor. In addition, it is also marked by the emergence of the microprocessor and semi-conductors. Companies that create micro-processors include: Intel Corporation, Motorola, Zilog, and others. In the market we can see the existence of a microprocessor from Intel with models 4004, 8088, 80286, 80386, 80486, and Pentium. Pentium-4 is the latest production from Intel Corporation that is expected to cover all the weaknesses that exist in previous products, in addition, the ability and speed of the Pentium-4 also increased to 2 GHz. The pictures were shown to be much smoother and sharper, in addition to the speed of processing, sending or receiving picture also becomes faster.
Pentium-4 manufactured using 0:18 micron technology. With the smaller form resulting power, current and voltage heat emitted is also getting smaller. With a faster processor cooler, can produce higher MHz speed. Owned speed is 20 times faster than a Pentium 3 generations.
Packard Bell IXTREME 4140i is one that has a PC computer using a Pentium-4 processor with a speed of 1.4 GHz, 128 MB RDRAM memory, a 40 GB hard drive (1.5 GB is used for recovery), as well as the GeForce2 MX video card with 32 MB of memory. The HP Pavilion 9850 is also a PC using a Pentium-4 processor with 1.4 GHz speed. PC Pentium-4 Hewllett-Packard is dating with predominantly black and gray. Compared to other PC, the Pavilion is a PC Pentium-4 with complete facilities. Owned by RDRAM memory 128 MB, 30 GB hard drive with at 17 inch monitors.
Broadly, the computer can be defined as an electronic device that consists of several components, which can work together between the components with one another to produce a program based on the information and data. The computer components are included: Screen Monitor, CPU, Keyboard, Mouse and Printer. Without a computer printer can still do its job as a data processor, but the extent has not been seen on screen in print form.
In such a definition there are tools such as slide rules, mechanical calculators types ranging from abacus and so on, until all contemporary electronic computers. The term better suited for a broad sense such as "computer" is "that process information" or "information processing systems."
Nowadays, computers are becoming more sophisticated. But, before the computer is not small, sophisticated, cool and light now. In the history of computers, there are five generations in the history of computers.
1. First Generation (1944-1959)

Vacuum tubes as a signal amplifier, is a hallmark of the first generation. At first, the vacuum tube (vacuum-tube) is used as a component of a signal amplifier. The raw material consists of glass, so many have drawbacks, such as: easy to break, and easy to distribute the heat. This heat needs to be neutralized by the other component that serves as a coolant.
And the presence of additional components, existing computer eventually becomes large, heavy and expensive. In 1946, the electronic computer in the world that the ENIAC was finished first. On the computer contained 18,800 vacuum tubes and weighs 30 tons. so great in size, to the point that requires a separate classroom.
In the images appear ENIAC computer, which is the world's first electronic computer which has a weight weighing 30 tons, a length of 30 M and 2.4 M high and requires 174 kilowatts of electrical power.
2. Second Generation (1960-1964)

Transistors are characteristic of second generation computers. The raw material consists of three layers, namely: "basic", "collector" and "emmiter". Transistor is an acronym for Transfer Resistor, which means to influence the survival of two of the three layers, the power (resistor) which is in the next layer can also be affected. Thus, the function of the transistor is as a signal amplifier. As a solid component, tansistor has many advantages such as: not easily broken, do not conduct heat. And thus, existing computers become smaller and cheaper.
In 1960, IBM introduced the first commercial computer that utilizes a transistor and is used widely began circulating in the market. IBM-7090 computer made in the United States is one of the commercial computer utilizing transistors. The computer is designed to solve all sorts of jobs both scientific and commercial. Because of its speed and ability, led to the IBM 7090 became very popular. Other second-generation computers are: IBM Serie 1400, Serie NCR 304, MARK IV and Honeywell Model 800.
3. Third Generation (1964-1975)

The concept of the smaller and more affordable than transistors, eventually spurring people to continue doing various studies. Thousands of transistors finally managed combined in a very small form. Yag silicium piece has the size of several millimeters successfully created, and this is referred to as integrated circuit or IC-Chip which is the hallmark of the third generation computers. The magnetic ring may be the magnetization in one direction or the opposite, and finally download sinyalkan condition "ON" or "OFF" which is then translated into the concept of 0 and 1 in the binary number system which is needed by the computer. In every field there are 924 ring of magnetic memory, each of which represents one bit of information. Millions of bits of information currently residing in one single chip with very small form.
The computer used for automation was first introduced in 1968 by PDC 808, which has a 4 KB (kilo-byte) memory and 8 bits for memory cores.
4. The Fourth Generation (1975-Present)

Microprocessor is a typical Chiri fourth generation computer which is compacting thousands IC into a Chip. Because the forms are getting smaller and increasing the capability and the price offered is also getting cheaper. Microprocessor is the beginning of the birth of the personal computer.
In 1971, Intel Corp later developed the first microprocessor serie 4004. An example of this is the generation of the Apple I Computer, developed by Steve Wozniak and Steve Jobs by inserting the microprocessor on the circuit board of the computer. In addition, later appearing with the TRS 80 Model type Motorola 68000 processor and Zilog Z-80 uses 64KB of RAM standard. Apple II computers that use e-6502R processor type and by 64 Kb Ram, also a very popular PC at that time. Operating systems used are: CP / M 8 Bit. This computer is very popular in the early 80s.
IBM Personal Computer began issuing in about the year 1981, using the MS-DOS Operating System 16 Bit. Due to the price offered is not much different from the other computer, in addition to the technology is much better and bigger than IBM's own name, then in a very short time, the computer is becoming very popular.
5. Fifth Generation (Now - Future)

In this generation is characterized by the emergence of: LSI (Large Scale Integration) which is the solidification of thousands microprocessor into a microprocesor. In addition, it is also marked by the emergence of the microprocessor and semi-conductors. Companies that create micro-processors include: Intel Corporation, Motorola, Zilog, and others. In the market we can see the existence of a microprocessor from Intel with models 4004, 8088, 80286, 80386, 80486, and Pentium. Pentium-4 is the latest production from Intel Corporation that is expected to cover all the weaknesses that exist in previous products, in addition, the ability and speed of the Pentium-4 also increased to 2 GHz. The pictures were shown to be much smoother and sharper, in addition to the speed of processing, sending or receiving picture also becomes faster.
Pentium-4 manufactured using 0:18 micron technology. With the smaller form resulting power, current and voltage heat emitted is also getting smaller. With a faster processor cooler, can produce higher MHz speed. Owned speed is 20 times faster than a Pentium 3 generations.
Packard Bell IXTREME 4140i is one that has a PC computer using a Pentium-4 processor with a speed of 1.4 GHz, 128 MB RDRAM memory, a 40 GB hard drive (1.5 GB is used for recovery), as well as the GeForce2 MX video card with 32 MB of memory. The HP Pavilion 9850 is also a PC using a Pentium-4 processor with 1.4 GHz speed. PC Pentium-4 Hewllett-Packard is dating with predominantly black and gray. Compared to other PC, the Pavilion is a PC Pentium-4 with complete facilities. Owned by RDRAM memory 128 MB, 30 GB hard drive with at 17 inch monitors.
Sunday, November 9, 2014
What is flash and its parts

Definition of Flashdisk
Flash Disk is the storage media from floppy driveB other types generally have a memory capacity of 128 MB s / d 64 GB, using interface types USBC (Universal Serial Bus), very practical and lightweight with sizes ranging from 96 x 32 mm and at the back of the form rather lead out, used for storage of AAA batteries and LCD (for Features MP3, FM Tuner and Voice Recording) and a USB port that provided the lid is shaped the same as the main body. Flash disks including tools of data pemyimpanan NAND type flash memory (Commonly used in Digital Camera), there is also packed in a small size into Compact Flash, SD Cards, MMC, and the like.
Parts of the flash
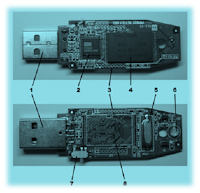 1 USB connector
1 USB connector2 Storage Controller Devices
3 Points Test (dots Experiment)
4 Chip Flash Memory
5 Crystal Oscillator
6 Indicator Lights
7 Write-Protect Switch
8 Space For Flash memory to 2
Main Components :
- FLASH MEMORY
- Microcontroller
Flash memory :
Flash memory is a type of EEPROM that allows plenty of memory locations to be erased or written in one programming operation. Lay terms: a form of memory chip that can be written, unlike the RAM chips, and holds its data without the need for electricity supply.
How it Works :
1) connector is used to connect peripherals contained in the flash drive into the USB port for later access by the SO.
2) memory storage controller functions to control and provide a link to a Flash disk apparatus in charge of maintaining stability of the device. The controller contains a small RISC microprocessor and almost the same on the RAM.
3) Then Point this test work for the check and send the code to the microprocessor
4) Once we create a file and save it on a flash drive then this section is the place to store data, typically also used in digital cameras.
5) This device generates 12 MHz signal from the main device and the control device data output to a phase locking ..
6) The indicator light is used to indicate the transfer of data or any data is read and written data.
7) Indicates whether the device is in the mode of "write-protection" or not.
8) The blank space provided for one additional flash memory, and can be used to store more data as needed.
Saturday, November 8, 2014
What is CPU?

CPU stands for Central Processing Unit, the computer hardware (harware) in charge of carrying out the orders and process data from the software. Often referred to as the processor, or computer brain. CPU itself is an internal component of a computer. CPU is small and square, containing some metal connectors on the bottom to be put directly into the CPU socket on the motherboard. Each motherboard only supports a certain type of CPU so you must check the motherboard specifications before attempting to replace or upgrade the CPU. Coinciding with the CPU generally also attached heat sink and small fan mounted directly on top of the CPU to help keep from getting too hot.
Components of the CPU
CPU consists of three components, namely :
- Control Unit, or the Control Unit, served as the control center of the computer that is taking a variety of data and instructions from memory for processing, selecting instructions related to arithmetic and logic functions and send it to the ALU for processing, supervises the work of the ALU, set up tools inputs and outputs, and bring back the results (output) processing to the main memory.
- ALU (Arithmetic and Logical Unit), for performing arithmetic and logic processes in accordance with the instructions of the program.
- Register, serves as a memory storage of data or instructions to be processed. The data from the main memory (RAM) is taken and then placed in a register, then data from registerlah processed.
Working Methods
 |
| wroking mthods |
List MicroPrcessor The General Unknown
Here is a list of commonly known CPU:
AMD : Athlon, Athlon 64, Athlon XP, Duron, Opteron, Sempron, Turion.
ARM : ARM.
Digital Equipment Corporation : V-11, MicroVAX 78 032, CVAX, Rigel, Mariah, NVAX, Alpha, StrongARM.
Elbrus : Elbrus-3.
Fairchild Semiconductor : Clipper.
Hewlett-Packard : Capricorn, FOCUS, PA-7000 ~ PA-8900, Saturn.
IBM : IBM 801, Cell Processor, Processor Broadway.
POWER : POWER 1 ~ 6, RISC Single Chip, P2SC.
PowerPC-AS : A10, A25, A30, RS64.
Intel : Itanium, Xeon, Core i5, Core i7, Core 2, Core, Pentium (Pro, MMX, II, III, 4, D, F, Dual-Core), Celeron, Atom.
MIPS Technologies : R2000, R3000, R3000A, R4000, R4400, R6000, R8000, R10000, R12000, R14000, R16000.
National Semiconducto r: NS320xx.
NEC : V20 / V25 / V40 and V30 / V33 / V50.
SPARC : SPARC.
Texas Instruments : TMS1000, TMS1100, TMS7000, TMS9900.
VIA : VIA, VIA C3, VIA C7, VIA Eden.
Western Electric : WE-32000.
Zilog : Zilog, Z80, Zilog Z8000.
The types of keyboards
The keyboard is an input device that is used to type information into a computer and run a variety of instructions or commands into a computer. The creation was inspired by the creation of a computer keyboard typewriter that basic design created by Christopher Latham in 1868 and marketed in 1877 by the Remington Company. The total number of keys on the keyboard there are 104 tombol.Keyboard have the same form and function with a typewriter.
The first computer keyboard adapted from the pit cards (punch cards), and writing long-distance delivery technologies (Teletype). 1946 ENIAC computer using a card reader makers holes (punched card reader) as input and output devices.
When you hear the word "keyboard" then the mind can not be separated from the existence of a computer, because the keyboard is a board consisting of the buttons to type in sentences and other special symbols on the computer. Keyboard in Indonesian means keyboard or keypad.
On the keyboard there are buttons letters A - Z, a - z, numbers 0-9, and special characters such as keys : `~ @ # $% ^ & * () _ - + = <> /,. ? :; "'\ | As well as other special buttons that total number is 104 buttons. While the machine is type in the number buttons 52 buttons. Bentukkeyboard generally rectangular, but the current model of the keyboard is very varied. The most famous keyboard is QWERTY keyboard that has 101 pieces of key (key). Most keyboards have keys that are arranged into the following sections:
A. Alphanumeric Key
B. Numeric Keypad
C. Function Key
D. Modifier Key
E. Cursor Movement Key.
Physically, the keyboard is divided into four types, namely:
1. Serial Keyboard
| serial |
Using DIN 5 of male and usually used on AT type computer.
2. Keyboard PS / 2
| PS / 2 |
3. Wireless Keyboard
| wireless |
As the name implies, this type does not use the keyboard as a liaison between the keyboard cable to the computer. This type of connection used is infra-red, wifi or bluetooth. To connect the keyboard to the computer, it takes the transmitter and receiver units. Unit transmitter is usually found on the keyboard itself, while the receiver is usually mounted on a USB or serial port on the CPU.
4. USB Keyboard
USB connector |
In shape and buttons, the keyboard is divided into seven types, namely:
1. QWERTY Keyboard
| QWERTY Keyboard |
The QWERTY keyboard layout found by Scholes, Glidden and Soule in 1878, and later became a standard commercial typewriter in 1905. QWERTY taken dari6 letter sequence in the second row of the alphanumeric keys. The QWERTY keyboard is designed such that the most commonly pressed keys located as far apart as possible, so to minimize the congestion at the time of typing (on a typewriter mechanic). Although the QWERTY layout is very widely used, but it has some weaknesses and inefficiencies. For example, 48 percent of the movement between successive letters have to do with a hand. Only 32 percent of beats done on the home row (row beginning from the position of the fingers on the keyboard). Greater burden left hand from the right hand (56 percent). The most obvious example of the inefficiency of the QWERTY layout is typing the letter 'a' is quite often used, but it must be done by the little finger is the weakest.
2.Keyboard Dvorak
| Keyboard Dvorak |
Dvorak Keyboard (1932), in which the arrangement of the letters are arranged such that the right hand burdened with more work than with the left hand. In addition, the Dvorak layout was designed so that 70 percent of the beats fall on the home row, which can reduce fatigue due to typing (more ergonomic). A number of experiments show that the Dvorak layout 10-15 percent more efficient than the QWERTY layout.
3.Keyboard KLOCKENBERG
| Keyboard KLOCKENBERG |
This keyboard is made with the intent enhance existing keyboard types, namely by separating the two halves of the keyboard (left and right). The left and right of the keyboard are separated by an angle of 15 degrees and sloped downward. In addition, the keyboard KLOCKENBERG have buttons made closer (thin) with a work table so it feels more comfortable. This layout, in addition to reducing the load on the muscles of the wrist and fingers are also designed to reduce the burden on the hand and shoulder muscles. Separation of the left and right making it relatively more space consuming.
4. Keyboard Maltron
| Keyboard Maltron |
Unlike the generally flat keyboard, this keyboard is made slightly concave inward. Considering that at the time the fingers are positioned to be typed, then the radius is guaranteed not to form a straight line. Manufacturers Maltron believes that basically, only used eight of the ten fingers available when a human finger typing with the keyboard typing on a regular keyboard always.With, the fingers have to adapt to the shape of the keyboard. It is claimed by them can cause RSI (Repetitive Stress Injuries). Meanwhile, by using Maltron, keyboardnyalah which will adjust by hand. With a unique shape like this, Maltron ensure comfort when typing fingers so as not to cause RSI can even be so because the increase typing speed used is 10 instead of 8 finger fingers.
5. Keyboard Chord
| Keyboard Chord |
Only have a few buttons from 4 to 5. To enter a letter have to press multiple keys simultaneously. The size is compact, it is suitable for portable applications. Short training time, Tombo-key emphasis reflects the desired shape speed is high but less popular, due to the long service will cause fatigue in hand. Here are the types of keyboard chord:
keyboard Palantype
Palantype layout has three groups of characters. The group on the left shows the initial consonant sebuuah words, the middle shows the vocal group and the right side shows the group the last consonant of a word or image kata.Pada rate seen that not all consonants are there, they will consonants can be presented using a combination of multiple buttons
keyboard stenotype
| keyboard stenotype |
Shorthand is a type of short writing that is often used to record the greeting. This type of writing most widely used by journalists to record interviews with faster results. Stenotype keyboards have advantages similar to the keyboard Palantype.
6. Keyboard Alphabetik
| Keyboard Alphabetik |
The buttons on the keyboard alphabetik arranged exactly as the QWERTY or Dvorak layout, but as a sequential arrangement of the letters in alphabetical order. Keyboard alphabetik also can not compete with the popularity of the QWERTY layout, but is usually found in many children's toys, so children were taught to know the alphabet letters. For users who are not typists, perhaps the layout is quite helpful. However, from the test results, the use of layout like this would slow down the speed of typing.
7. Keyboard Numeric
| Keyboard Numeric |
To enter numbers in large numbers, people prefer to use the numeric keypad (numeric keypad) the layout of its buttons can be reached by hand.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
